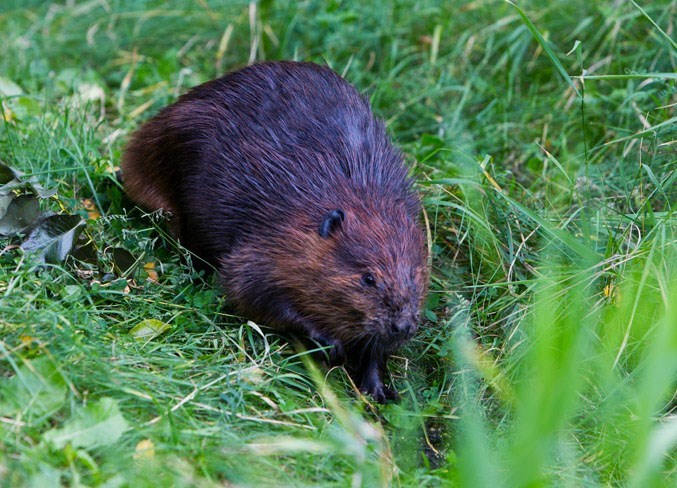
London’s New Rewilding Project Includes Plans To Reintroduce Beavers To The Capital
London soon may soon be the place to be for those hoping to catch sight of beavers working at Paradise Fields in Greenford.
By JACK SADDLER, SECRET LONDON

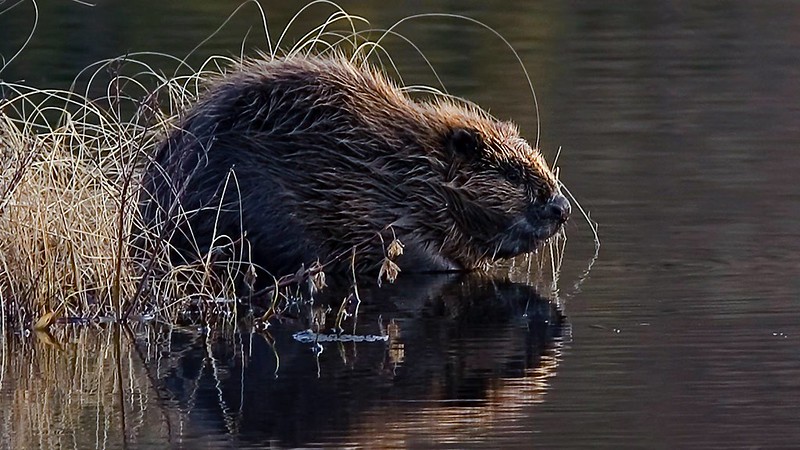
Should you ever wish to travel back to the times of the Tudors in London, you’ll probably notice significantly more folks on horseback and rows of half-timbered houses. It also will beam you to a time where beavers could be seen scuttling around riverbanks, doing their dam thing.
Sadly, the rodents were eventually hunted to extinction for their fur and meat, but after more than 400 years, it looks like the boys beavers are back in town.
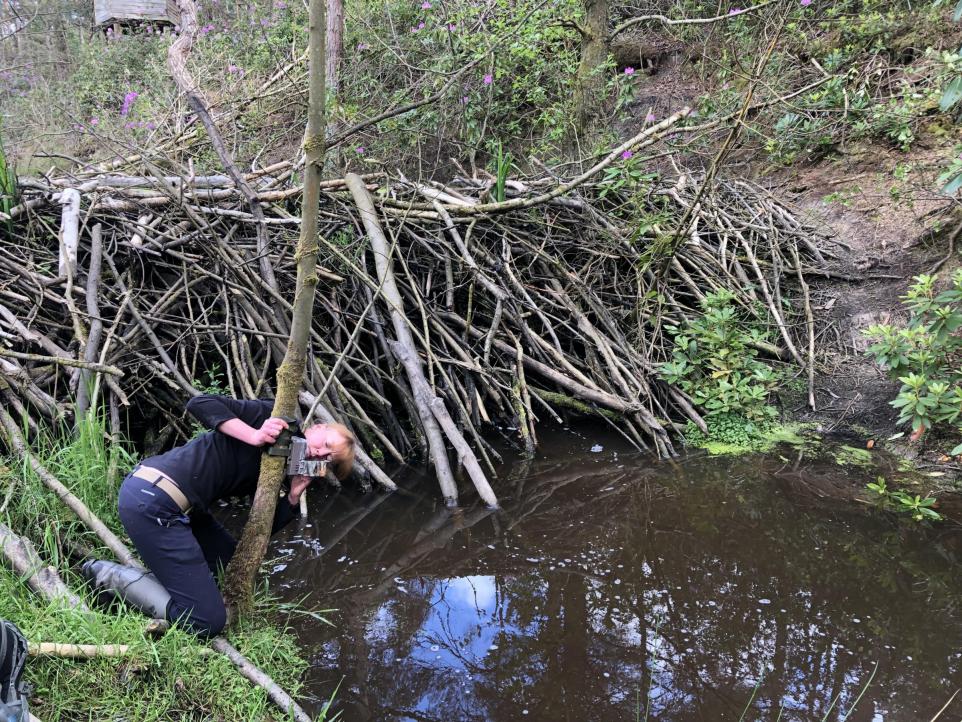
Come this Autumn, London will have its first beaver habitat that’s accessible to the public, when Paradise Fields in Greenford welcomes a breeding pair, who will arrive alongside their kits (infants).
It comes—handily, on World Rewilding Day!—as part of major plans to rewild London, with conservation groups receiving nearly £40,000 in funding from City Hall to create this habitat for beavers.

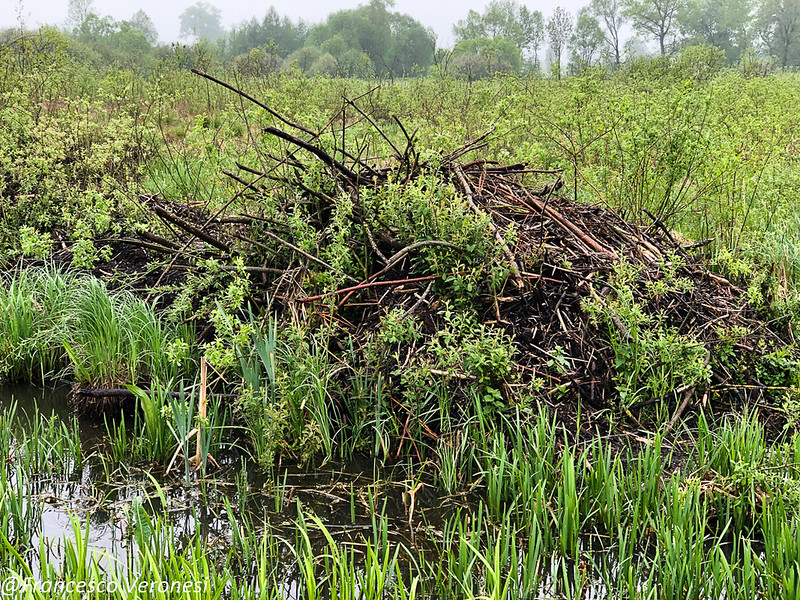
Eventually, this area will become a ‘beaver safari’ for visitors to view the rodents, who are known for their vegetarian diet and their dam-building prowess. It is hoped that this skill will be useful to quell flooding in England made worse by climate change.
Beaver enthusiasts may recall some talk of beavers arriving in London last year as part of rewilding plans, and they were, in fact, introduced in Enfield. Sadly, the male beaver – who was named Justin Beaver (!) and arrived alongside his partner, Sigourney (!!) – passed away due to natural causes three months into the rewilding scheme.
A second beaver is said to have been welcomed at Forty Hall farm in north London, though Paradise Fields in Greenford will welcome more beavers as part of this first ‘beaver safari’ later this year. This safari is part of a new wetland planned in Ealing by Citizen Zoo, Ealing Wildlife Group, Ealing Council and Friends of Horsenden Hill.
In a press release, Nick Swallow, Citizen Zoo Fundraising Operations Officer, said: “Across Europe and North America, beavers are known to thrive alongside urban communities.
“…We hope to challenge the perceptions of Londoners and demonstrate how London too, can embrace these ecosystem engineers as we strive for a healthier, wilder future in which our Capital can become a leader in urban rewilding, which will greatly benefit not only wildlife populations but local communities too.”
“We’re cleaning up our city, re-establishing lost species and reconnecting people and nature as we build a greener, fairer city for all Londoners.”
Property owners in Muskoka responsible for beaver dam damages
Beavers can have positive impacts — and negatives ones — on your land
By Brent Cooper, Gravenhurst Banner
Cliff Samson has a love-hate relationship with his “neighbours” along Pigeon Creek.
“Behind my property here, I’ve got a nice pond creek that’s running all year, and I’ve got all kinds of animals and whatnot for the past, probably seven years.”
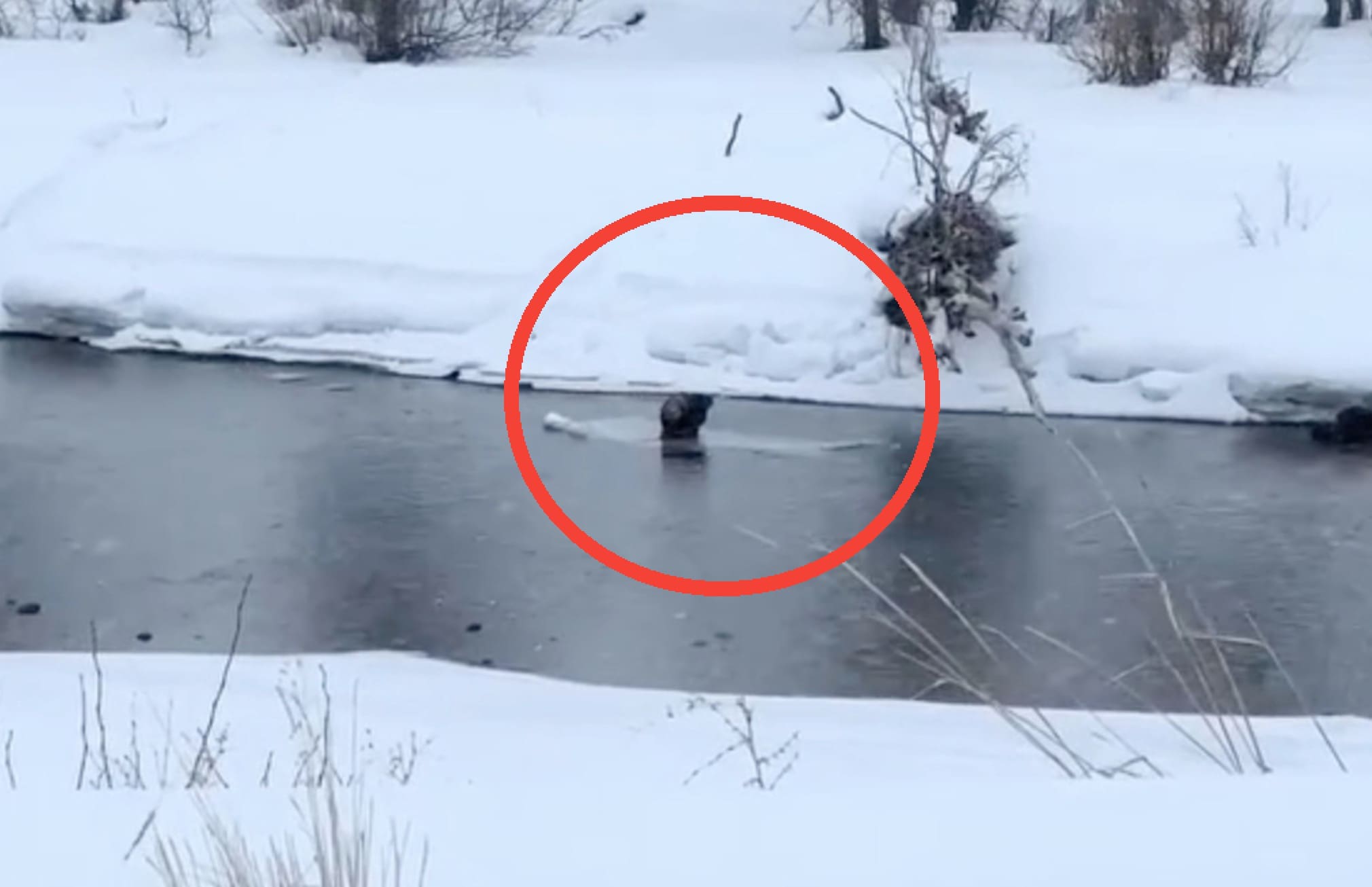
Then one day in the past few years, his “neighbours” moved in … or more precisely, beavers began to build homes and dams on the creek, and according to Samson, there are some good points of having these industrious critters nearby.
“What ends up happening is that there’s a natural waterfall down at the other end and in the summer months, when it’s dry, there’s no water coming over that. Without the beaver dam at this end, all my water would drain out, and I would basically have a marsh behind my house with no water in it. But because of the beaver dam, it keeps water here all the time. And as a result, I’ve got wildlife here all the time.”
While the beavers do allow Samson and his family to enjoy regular visits by various wildlife caused by the flowing water, the situation does come with some overflow issues.
According to the Ministry of Northern Development, Mines, Natural Resources and Forestry, it is illegal to damage or destroy a beaver dam unless specifically exempted through the Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act, such as for the removal of dams to protect private property.
“When a landowner elects to remove a beaver dam, the landowner or agent must exercise extreme caution to prevent downstream flooding, damage to natural habitats and property damage,” said Amanda Vincent, resource management co-ordinator for the ministry.
So what should a property owner do if they spot a beaver dam on their property that could cause infrastructure damage?
The ministry said property owners can make the area uninviting for beavers by planting vegetation that beavers don’t like, such as elderberry, ninebark and twinberry; wrapping individual trees in metre-high, galvanized welded wire fencing, hardware cloth or multiple layers of chicken wire; or painting tree trunks with a sand and paint mix to protect trees from beaver damage.
One can also hire an experienced trapper or wildlife technician to properly remove the beavers from the region. [But we’ll be back!] ![]()
In cases of flooding due to a blocked waterway or culvert, some experts recommend using a beaver deceiver, a structure that utilizes a plastic culvert and heavy-duty fencing installed in the beaver dam, allowing water to drain to a lower level.






 Beavers! They’re baaack! Beavers are amazing animals. Hear about their incredible physiology,
Beavers! They’re baaack! Beavers are amazing animals. Hear about their incredible physiology,