Linksploration – Bay Area
Exploring the many paths to a greener future
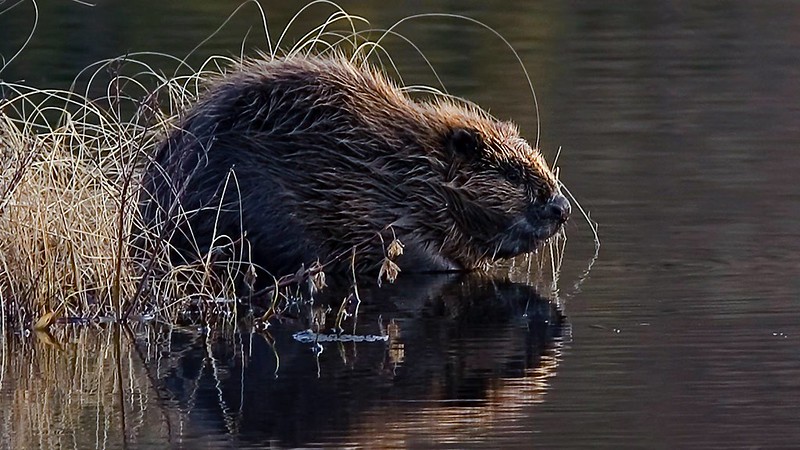
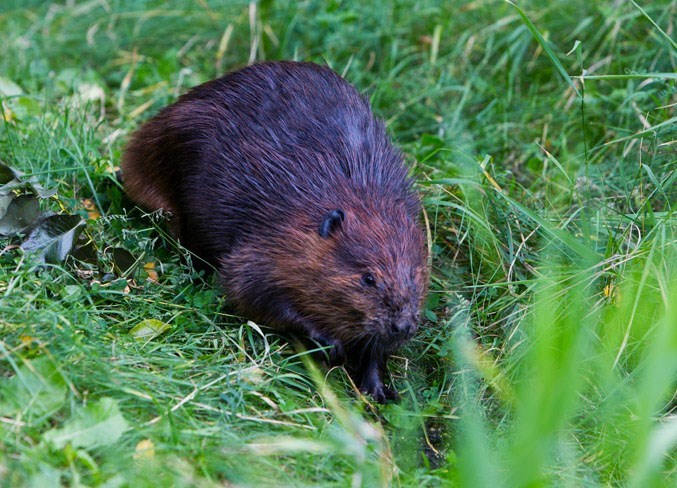
 Beavers! They’re baaack! Beavers are amazing animals. Hear about their incredible physiology, Heidi Perryman and Mitch Avalon relate the story of the Martinez beavers, and what’s next for them in the Bay Area.
Beavers! They’re baaack! Beavers are amazing animals. Hear about their incredible physiology, Heidi Perryman and Mitch Avalon relate the story of the Martinez beavers, and what’s next for them in the Bay Area.
Beavers reclaim land in southeast Michigan
Marina Johnson, Detroit Free Press
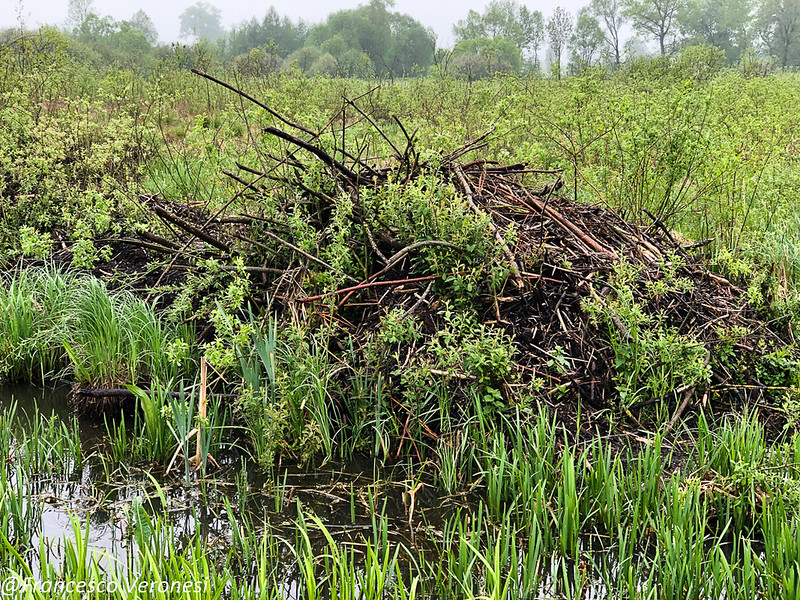
Over the past decade, beaver populations have returned to southeast Michigan in places such as Belle Isle, Stony Island, the Conner Creek Power Plant and other places along the Detroit River.
Why did beaver populations decline?
When settlers moved into metro Detroit, beaver trapping for the fur trade was plentiful, eliminating much of the population. The existence of this species was almost wiped out due to 300 years of trapping and trading. Along with trapping, industrialization and habitat loss pushed beavers out of the area and they were last reported in 1877 as a result, said Great Lakes Now.
When did beavers return to the area?
Beavers were first reported back in the area in 2008, according to Friends of the Rouge. For the first time in over 100 years, beavers gnawed away at trees and built damns near Conners Creek Power Plant. Since then, beaver sightings in the Detroit and Rouge Rivers aren’t uncommon and continues to increase.
![]() But not necessarily welcome throughout.
But not necessarily welcome throughout.
Are beavers good for urbanized areas?
The DNR has beavers categorized as nuisance wildlife due to damage caused in urban and industrialized areas. They often gnaw on trees and their damns cause flooding and problems for homeowners. The DNR does offer trapping services and permits for those impacted in certain areas.
Cooley wrote the DNR is given a difficult hand because they want beavers around but not at the expense of someone’s property.
“Beaver in residential areas typically lead to problems, it’s their nature to back up and flood a waterway to create a pond,” he wrote. “Up North or out in the country, they can do that and it doesn’t impact anyone, most people would never even know it happened. However, down here in southeast Michigan if they back up a drain or a river, it is eventually going to flood someone’s yard and possibly impact their house.”
Read the whole article here. ![]()
Better acceptance in Cropton:
Cropton Forest beaver project by Forestry England proving successful
A trial project that’s re-introduced beavers to a forest in North Yorkshire is going from strength to strength as it enters its final year.
By Leigh Jones, The Northern Echo
The Cropton Forest beaver project, which saw two beavers released on enclosed land upstream of Sinnington in April 2019, has been credited with helping to reduce the flood risk for the village and for transforming the ecology of the area for the good.
The five year project, which is overseen by Forestry England, hopes to examine the impact of re-introducing beavers to the wild in England after they were hunted to extinction in the sixteenth century. It’s one of a number of pilots across the UK which have support from a number of organisations including the RSPB.
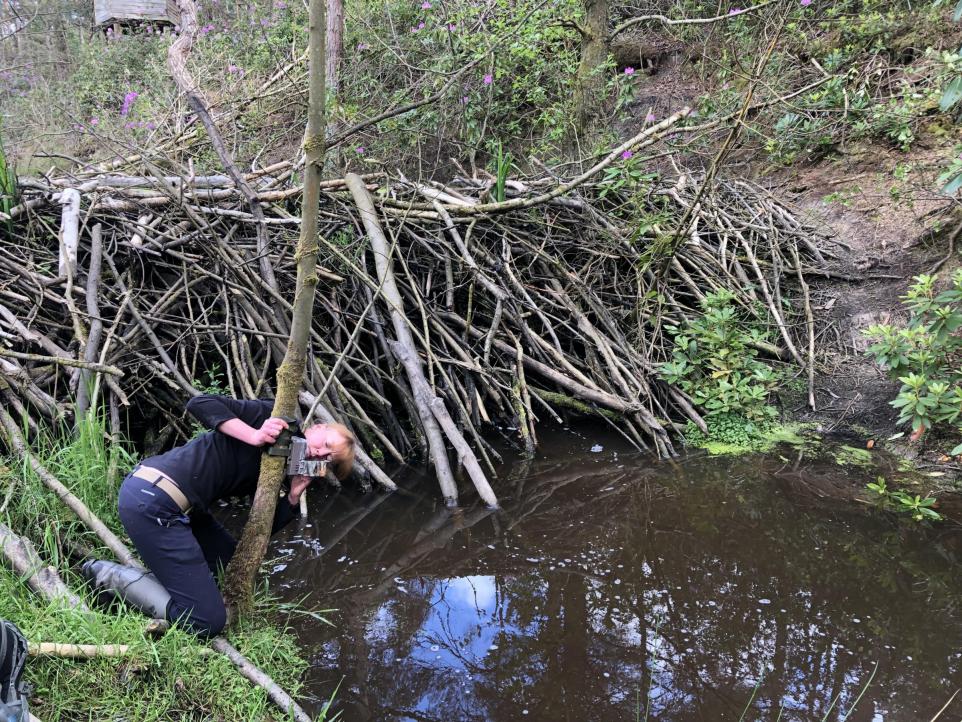

At the centre of the North Yorkshire beavers’ habitat is an enormous 70m long dam that the original beavers have built over the years alongside the kits that they’ve had since being re-introduced to the area four years ago.
Ecologist Cath Bashforth, who leads the project, said that the pilot has “far exceeded what we expected.
“We never expected such a dramatic impact in such a short space of time.”
In terms of the dramatic impact, the slowing of water flow through the site helps protect downstream areas from flooding, however the beavers’ presence has a knock on effect in many areas surrounding their habitat.
“At the start of the trial we had some fantastic volunteers who helped us take a baseline biodiversity survey to examine what impact the beavers would have,” says Cath.

Having built their enormous dam along with five or six smaller ones Cath is optimistic that the beavers will be able to stay in North Yorkshire on conclusion of the pilot scheme.
As the project looks to reach its conclusion in a little over a year, the fate of the beavers presently on site remains undecided.
Read the whole article here. ![]()
And you might want to add this to your calendar:
Posted on The Ukiah Daily Journal
Peregrine Audubon Society to present The Beaver Believers program
Peregrine Audubon Society Program will be hosting a zoom presentation on Tuesday, March 21 at 7 p.m. featuring The Beaver Believers hosted by Sarah Koenigsberg of the Beaver Coalition.
In this film, we follow our Beaver Believers out into some truly spectacular landscapes of the interior West, from the east slopes of the Cascade mountains in Washington to the Rockies in Colorado, from the parched red rock deserts of southern Utah to an urban park in central California.
We take you to places where beaver have already begun to transform damaged watersheds, and we learn of the many challenges that stand in the way of larger scale efforts to use beaver as a restoration tool, including trapping, which is tragically still legal in most states.
Perhaps most importantly, we meet incredible people who, undaunted by climate change, are working tirelessly to protect and restore beaver out on the landscape, who embody the spirit and joy that comes from “thinking like a beaver,” who show us that collaboration and watershed restoration truly are possible. All we have to do is let the beaver come home.
The coalition is dedicated to strategically advancing a paradigm shift in society’s relationship with beaver. Learn more at beavercoalition.org
Lastly, from Unofficial Networks:
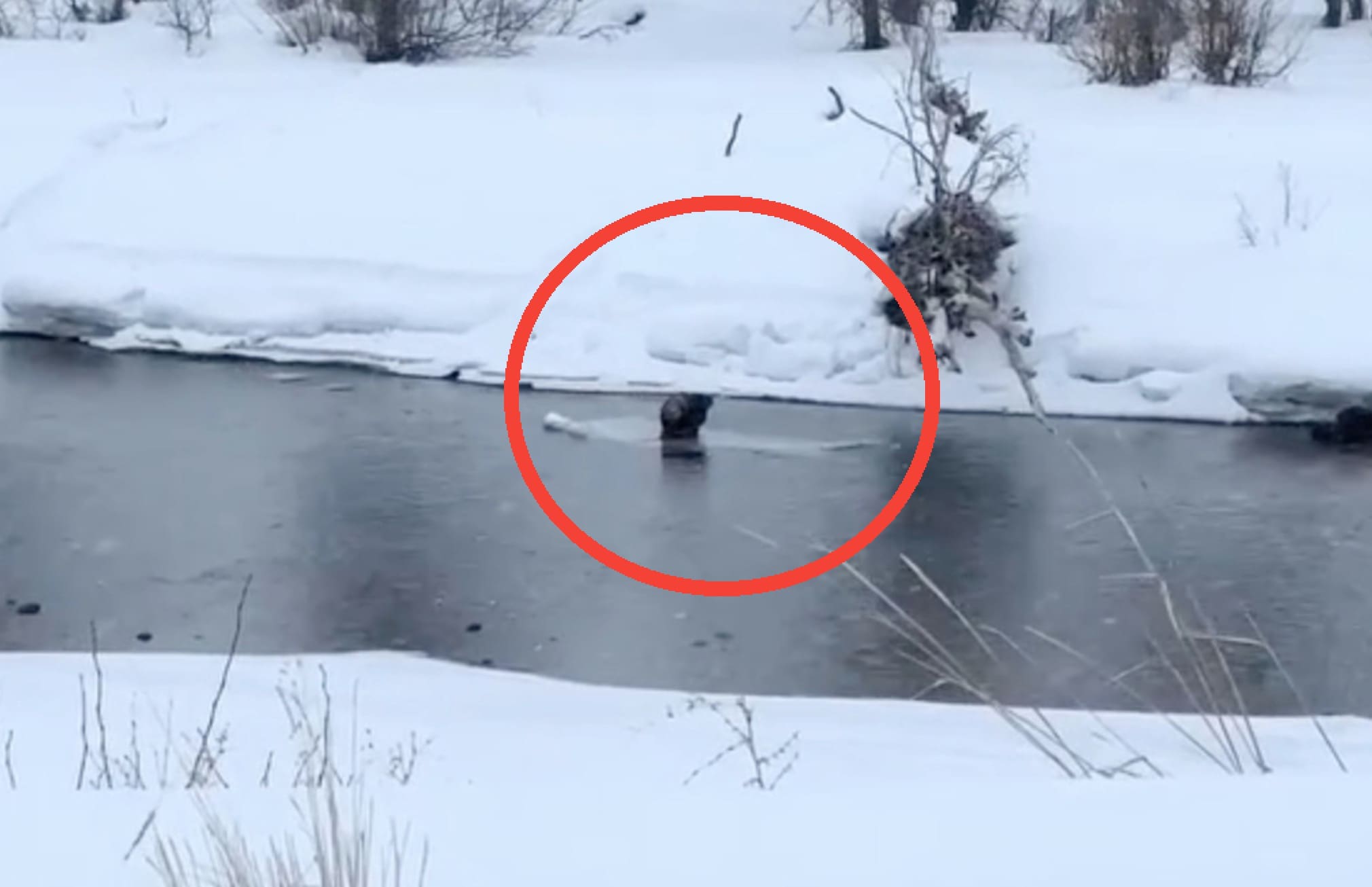

The cute video that the image above is taken from is by nature photographer Nick Sulzer.