Alright. We’ve sufficiently mocked the beaver wildfire article and now we can get down to the good stuff. Just so you know in the background our tech-wizard Bruce Mushrush is busily migrating the beaver summit site to ours so that we won’t have to pay for both. If things are busy or weird for a moment just come back in a few minutes and all will be well. Because there are GOOD THINGS TO DISCUSS!!!
Scientists EEAGER-ly Track Beavers Across Western United States
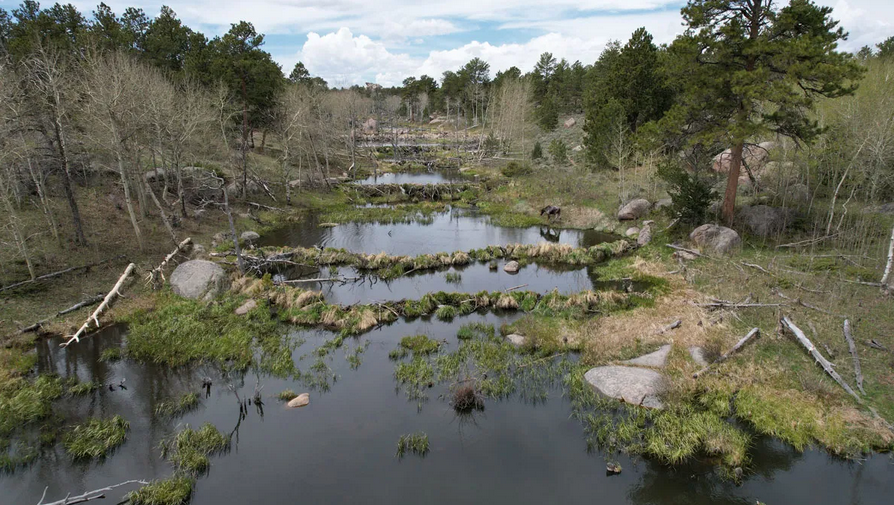 Beavers are among the world’s most effective engineers. Members of this keystone species build dams and canals and, in so doing, create entire, multilayered wetland ecosystems. Beginning in the 1600s, however, the fur trade decimated North American beaver populations.
Beavers are among the world’s most effective engineers. Members of this keystone species build dams and canals and, in so doing, create entire, multilayered wetland ecosystems. Beginning in the 1600s, however, the fur trade decimated North American beaver populations.
The species began rebounding in the early 20th century but sometimes came into conflict with the agricultural landscape, as by the 1940s and 1950s, people were aggressively modifying streams to maximize yield. Returning to their former haunts meant persecution as beavers flooded crops and felled orchards, explained Alexa Whipple, program director for the Methow Beaver Project (part of a nonprofit called the Methow Salmon Recovery Foundation).
Now, humans are starting to recognize that beavers, though still considered pests by some, benefit landscapes in myriad ways. For instance, beaver activity can reduce erosion, create habitat for other species, and maintain wetlands.
I’m liking where this is going. Surely we are going to enjoy todays read more than hitting the ecosystem over the head with a hammer.
In fact, we often want beavers to move back into landscapes to do the engineering for us, said Emily Fairfax, an assistant professor at California State University, Channel Islands. “But how are we going to know if they are doing that,” she asked, “if we don’t even know where they are?” The answer lies in remote sensing imagery, which can help scientists identify the landscape-scale features created by beaver families.
Through a combination of fieldwork and remote sensing, Fairfax tracks where beavers reside across the western United States. To make the process more efficient, she’s working with Google Earth Engine to develop the Earth Engine Automated Geospatial Element Recognition model—aptly called EEAGER—which uses machine learning to rapidly identify beaver dams in satellite and aerial imagery.
In work presented at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2022, Fairfax found that EEAGER decreased the time needed to map beaver dams by about 80%. By rapidly finding beaver ponds and comparing their changing distribution over time, scientists like Fairfax can track beaver populations to quantify the effects of their environmental engineering.
This years ago I got a call from an environmentalist working on the google sustainability team and he mentioned the tech giant was interested in adapting their “space laser technology” to id beaver habitat from space. And I was very impressed but daunted as to how it would work or where to offer such a skill. It is wonderful to see it find a home with Dr. Fairfax and the AGU.
 The amount of existing and incoming imagery isn’t an impediment for sky-based beaver surveillance. Beaver dams remain in place for 5 to 7 years on average, said Fairfax; very high resolution data that are publicly available come out at least every couple of years and sometimes more often when fires and droughts strike (which is becoming more common). Lower-resolution data sets can provide helpful imagery about once per week, filling in any gaps.
The amount of existing and incoming imagery isn’t an impediment for sky-based beaver surveillance. Beaver dams remain in place for 5 to 7 years on average, said Fairfax; very high resolution data that are publicly available come out at least every couple of years and sometimes more often when fires and droughts strike (which is becoming more common). Lower-resolution data sets can provide helpful imagery about once per week, filling in any gaps.
However, tracing beaver dams in such imagery is incredibly time-consuming, often taking weeks to months. With large quantities of imagery, which Fairfax noted is a pleasant problem to have, the process can become a nightmarish sea of external hard drives holding terabytes of data.
Fairfax and her colleagues at Google who specialize in neural networks, machine learning, and artificial intelligence trained the EEAGER model with 8,000 of Fairfax’s manually identified beaver dams and another 5,000 from other coauthors. Because the model was convinced that cul-de-sacs were also beaver dams, they had to train the model on “not dams” as well.
All those little engineers being watched over by all those other little engineers! It’s fun to imagine, isn’t it? My nephew works for google. Do you think he’s part of the team?
EEAGER can now sort through massive amounts of satellite and aerial imagery and identify pixels that contain evidence of beaver activity. With Google Earth Engine, the data querying and processing happen in the cloud, Fairfax explained, so she doesn’t need to add more hard drives to her already impressive stash.
Fairfax noted that the model wouldn’t work as well as it does without extensive field mapping of beaver dams (and not beaver dams), which involves wading through muck and dense vegetation. But although pond-specific beaver studies are important, looking at how beavers affect entire watersheds can now be efficiently accomplished in beaver-based research.
For regions still needing ground truthing, drones now expedite this process. However, because Fairfax’s research has been focused on the western United States, EEAGER may be biased. “We actually don’t know how good it would do in places like Canada or Minnesota,” she said, “because it hasn’t been trained there.”
Computers trained to be on the lookout for beavers! Now if only we could train HUMANS to be on the lookout for beavers in the sense of welcoming them when they arrive.
After the results from EEAGER go through quality control, calculations can address whatever the science question at hand may be. For instance, in research currently under review, Fairfax looked at whether beaver dams became fire refuges during three Rocky Mountain megafires in 2020. In some watersheds, beavers had dammed every single stream from start to end, she said. These sinuous stretches of hydrologic connectivity resulted in fire-resistant habitats. “In these beaver complexes, everything stays wet,” said Fairfax, which means fires cannot easily burn these ponds.
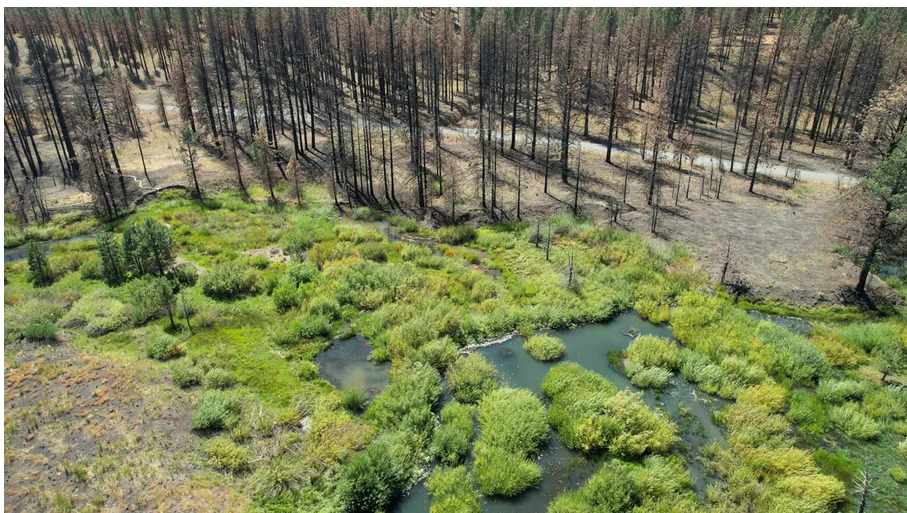 “I’ve gone to [wildfire] sites where I fully expected the beavers to be dead,” she recalled, but “the evening rolls around and the beavers come swimming out.”
“I’ve gone to [wildfire] sites where I fully expected the beavers to be dead,” she recalled, but “the evening rolls around and the beavers come swimming out.”
Channel modifications, such as straightening bends to transport logs and barges, result in water being whisked rapidly downstream, said Chris Jordan, a research fisheries biologist with NOAA’s National Marine Fisheries Service who was not involved with the study. Beavers’ networks of dams, canals, and felled trees do the opposite, slowing water down, which—like magic (except that it’s physics)—restores river systems, he said.
Given time and opportunity, beavers will engineer an entire valley floor, which could be more than a kilometer wide, said Fairfax. That seemingly magical engineering lets water seep into the soil, allowing streams to reconnect to their floodplains. Simple or degraded ecosystems can transform into riverscapes with healthy food chains.
You know how they do, hitting the ecosystem over the head with a hammer and all. Looks like Emily can tell the difference between a beaver effect and a wildfire.Maybe she should sit down with Ken Tape.
For example, because endangered salmon and similar fish species are born and die in fresh water, they depend on healthy river conditions to complete their life cycle, Jordan said. Growing more fish requires ants, earthworms, and other floodplain-dwelling invertebrates to become fish fodder. But for that part of the food chain to exist, landscapes around rivers need to be wet at least some of the time. Beavers create the necessary wetland environments that then become biodiversity hot spots.
Regular snapshots of beaver ponds from space, combined with algorithms doing the tedious work of examining millions of kilometers of streams, means new ways to quantify the impact beavers are having on the landscape, Jordan said.
Yes. You just keep algorithm-ing away and beavers will keep beavering away and maybe some day humans will finally understand why they should appreciate them.
I for one can hardly wait.