One of the advantages of having ‘beaver buddies’ all over the world is that there is almost always someone on hand to help me get the things I cannot reach. Like this, intriguing headline that requires a paid subscription or a passport to unravel. Fortunately for me, Chris Brooke of the Save the Free Beavers of the Tay FB group leaped to the rescue:
 Beaver fever proves giant rodents are not a dam nuisance
Beaver fever proves giant rodents are not a dam nuisance
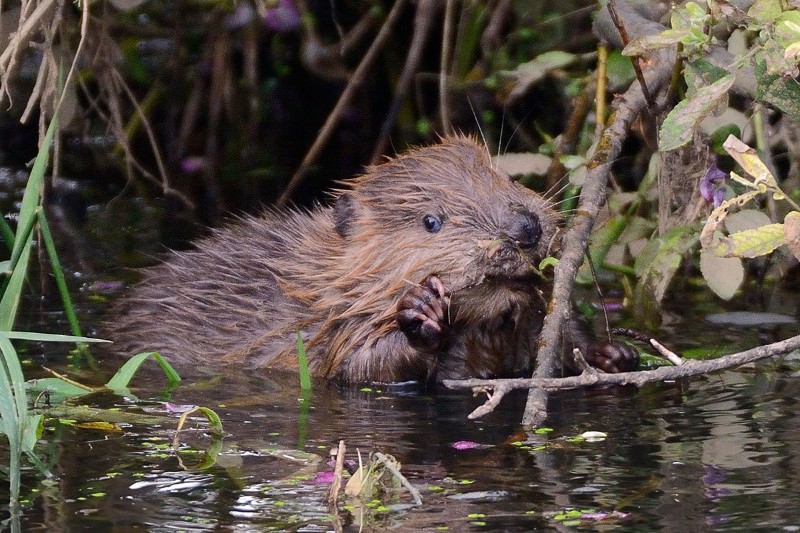
 It is a wonder that anyone wants to reintroduce beavers almost 400 years after they were hunted to extinction. They sound like a farmer’s nightmare, creating soggy fields, rotten trees and pools of standing water, and infuriate anglers, as their dams are believed to hinder fish migration.
It is a wonder that anyone wants to reintroduce beavers almost 400 years after they were hunted to extinction. They sound like a farmer’s nightmare, creating soggy fields, rotten trees and pools of standing water, and infuriate anglers, as their dams are believed to hinder fish migration.
Yet a study into their effect on flooding on a farm in Devon has led to “beaver fever”, a clamour for more, not fewer, of the huge rodents and similar trials across England.
Beavers’ dams control the flow of water after rain and act as natural filters of chemical fertilisers that run off fields. In summer they also stop streams drying up, according to researchers at Exeter University, while coppicing trees creates a patchwork of different habitats that has increased the range of plants and wild animals.
Ooh I’m liking the way this is going. Time for coffee and a comfortable chair while I explore further. Mind you, this is the largest selling ‘respectable paper’ in ALL of the UK, so I think there are going to be folks paying attention. Including all the magistrates, farmers and anglers.
Richard Brazier, who led the initial research, has been asked to carry out six feasibility studies for beaver projects in Dorset, Gloucestershire, Devon and Cornwall. “The science suggests it would benefit society to have beavers in the landscape,” he said.
Naturalists in Wales have applied for permits to release ten pairs in Carmathanshire, while beavers in Scotland have been granted native species status after similar trials in Argyll.
In Devon, the beavers built 13 dams on a 180m stretch of stream inside an enclosure. Water flowing out had 30 per cent less nitrogen than water flowing in, almost 70 per cent less sediment and 80 percent less phosphates.
“Fertiliser getting washed out of soils is a huge problem worldwide,” Professor Brazier said. “It leads to algal blooms that starve the water of oxygen, which leads to fish deaths. It’s one of the reasons we have to treat our drinking water.”
If the difficult beavers of South America are the nagging critical aunt of the beaver world who’s petty complaints you just can’t escape, the epic “TO BEAVER OR NOT TO BEAVER” struggle of the UK is that glowing fountain of praise from your indulgent grandmother. I love hearing them argue about this over and over again because they are repeating the pro’s with a megaphone on an international scale. I don’t want them to ever stop, because who will take their place?
The government has promised £2.5 billion for improved flood defences, including £15 million for natural flood management such as planting trees and adding bends to rivers which have been artificially straightened.
“Most of the money is being spent on concrete,” said Chris Jones, a farmer, who is planning to release beavers upstream of Ladock, in Cornwall, a village that was flooded twice in 2012. “We need our land to store more water, so we don’t have these massive pulses of water after every heavy rainfall.”
Not everybody is a fan of the animals, which can grow to 25kg. A spokesman for the Angling Trust criticised “adding more barriers to fish migration”, while the NFU opposes beaver reintroductions because of “damage to farmland … and the risks of them spreading disease”.
Mark Elliott, of Devon Wildlife Trust, said that farmers’ “biggest concern is that beavers will become a protected species. If they are going to be accepted by landowners, there have to be clear mechanisms for managing the conflicts [between the two].”
Really Mark? Is that really your ‘biggest concern’? That beavers will be protected? Wouldn’t a bigger concern be that there wouldn’t be beavers at all? Or that all your rivers will dry up and that global warming will make it too arid to have them there anyway? Or that Theresa May will turn out to be exactly like Trump. How could the protection of beavers be your BIGGEST concern?
 Okay, I’ll give Mark a break. Maybe that was a misquote or taken out of context. Maybe you’re having an off day or your cat is in the vet. It’s mostly a wonderful article. And I’m still very happy about it. We all should be!
Okay, I’ll give Mark a break. Maybe that was a misquote or taken out of context. Maybe you’re having an off day or your cat is in the vet. It’s mostly a wonderful article. And I’m still very happy about it. We all should be!



 ence, every species – plant and animal– depends on the behaviour of just one: the
ence, every species – plant and animal– depends on the behaviour of just one: the 
 p, Brazier says. By slowing the flow – while storing 650,000 litres of water behind each dam – these mammals are a natural method of flood prevention, before the flood has even started. They can protect our homes, by building their own.
p, Brazier says. By slowing the flow – while storing 650,000 litres of water behind each dam – these mammals are a natural method of flood prevention, before the flood has even started. They can protect our homes, by building their own.