The San Francisco Estuary Partnership does remarkable work coordinating and educating partners around the East Bay. They were the first significant friend our beavers made in the real world and they are how I met Lisa Viani who was then the editor of their magazine and eventually reporter Joe Eaton and the famous Ann Riley who was special consultant of the SF Waterboard. Ann eventually brought me to
The San Francisco Estuary Partnership does remarkable work coordinating and educating partners around the East Bay. They were the first significant friend our beavers made in the real world and they are how I met Lisa Viani who was then the editor of their magazine and eventually reporter Joe Eaton and the famous Ann Riley who was special consultant of the SF Waterboard. Ann eventually brought me to  Oakland for a very important talk to other board members. which introduced us to the watershed stewards of Americorp who helped our festival for years and worked to replant trees at the creek.
Oakland for a very important talk to other board members. which introduced us to the watershed stewards of Americorp who helped our festival for years and worked to replant trees at the creek.
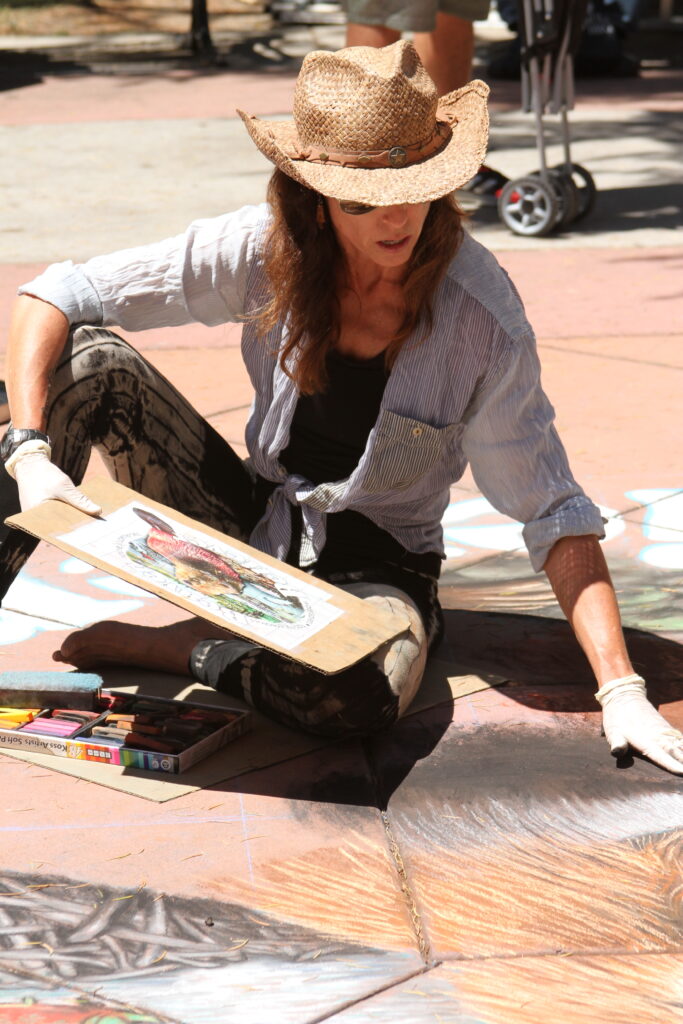
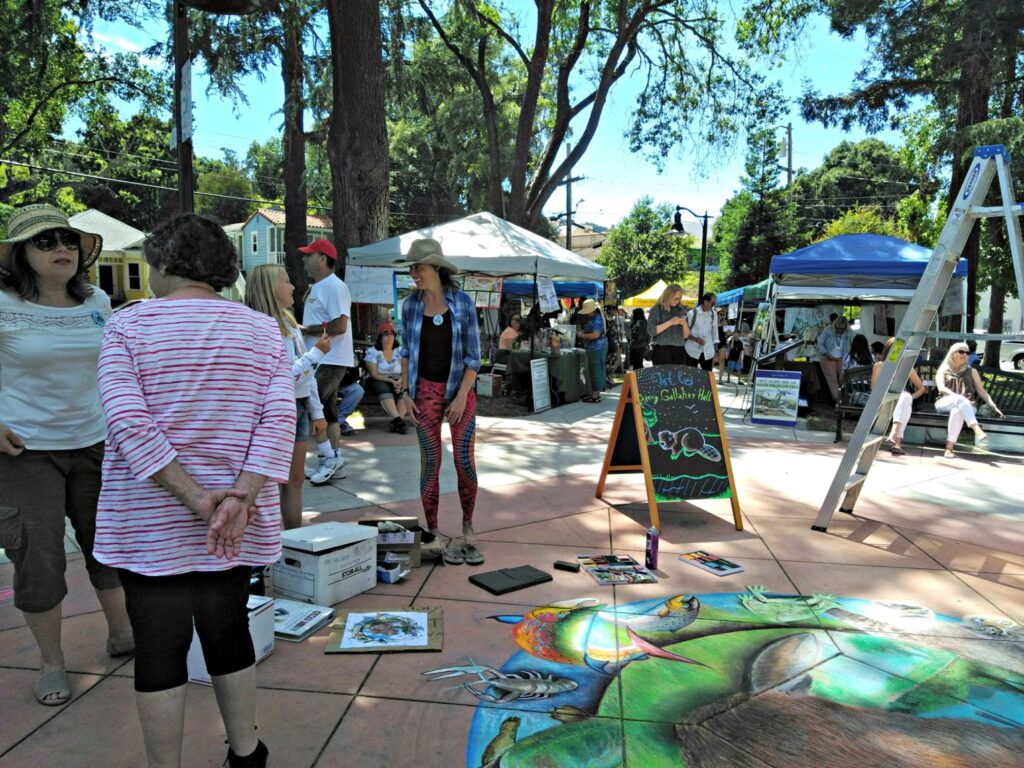
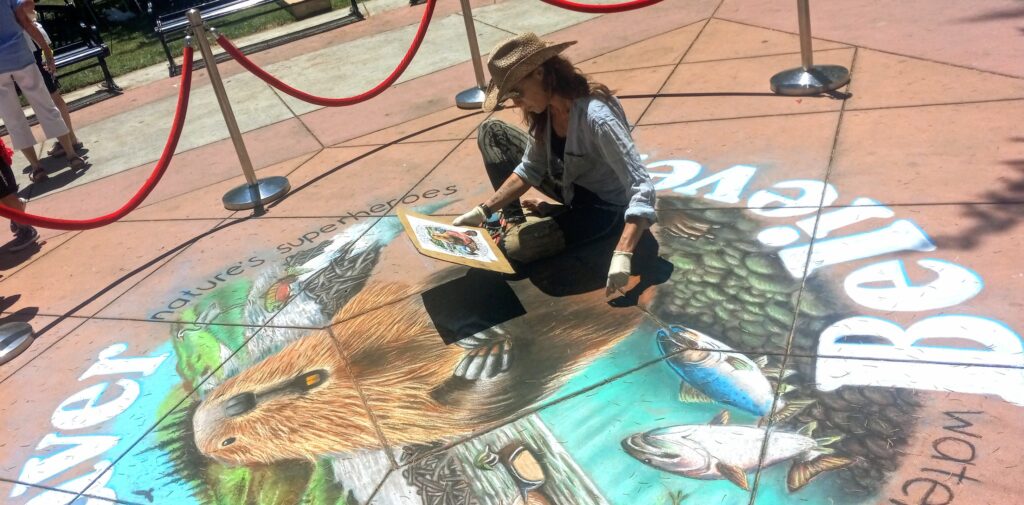
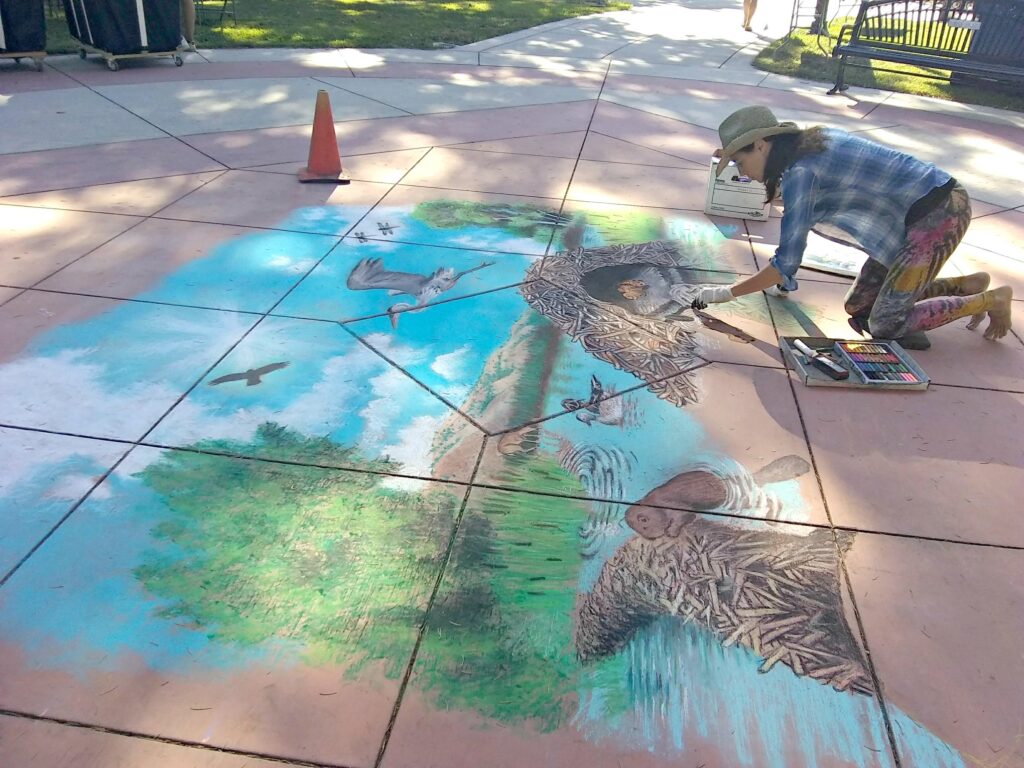
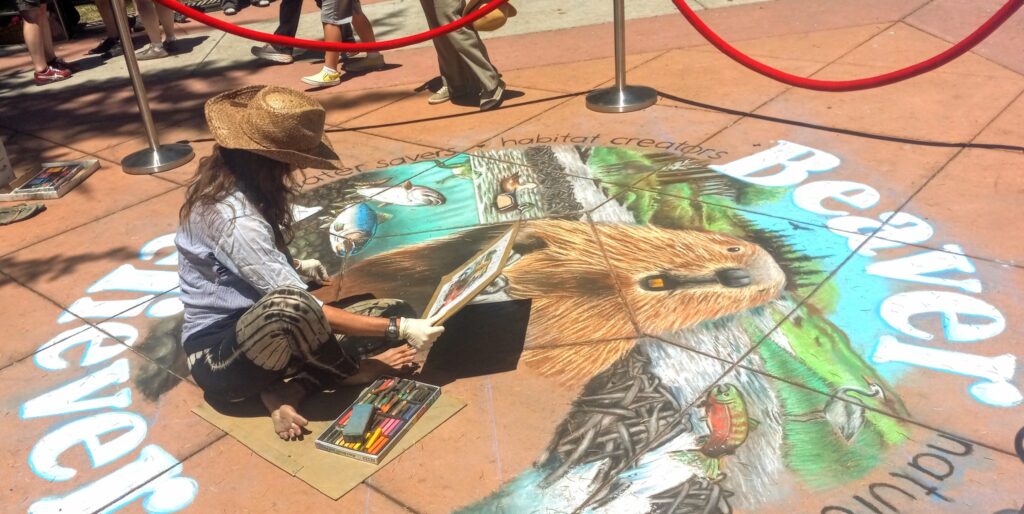
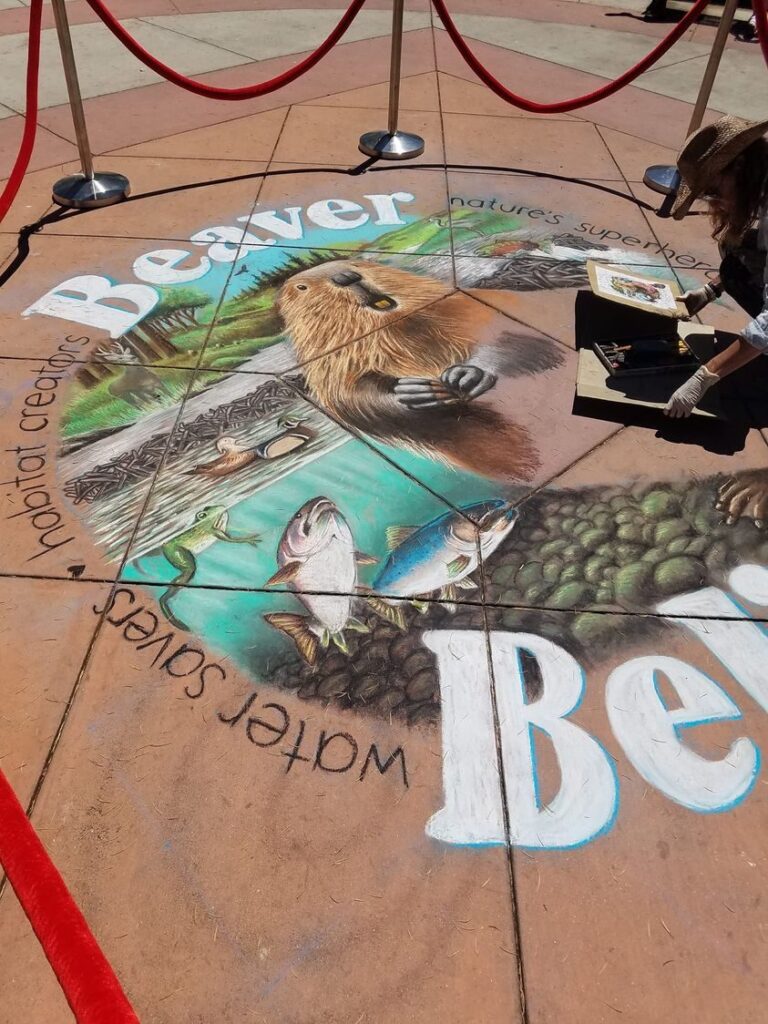
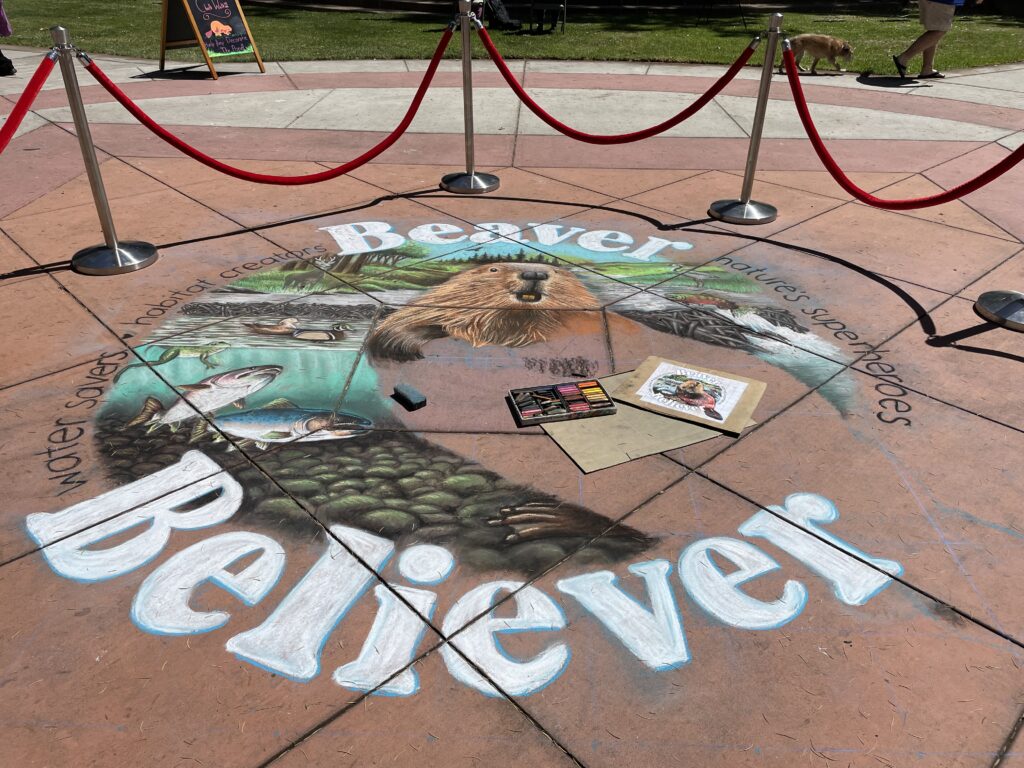
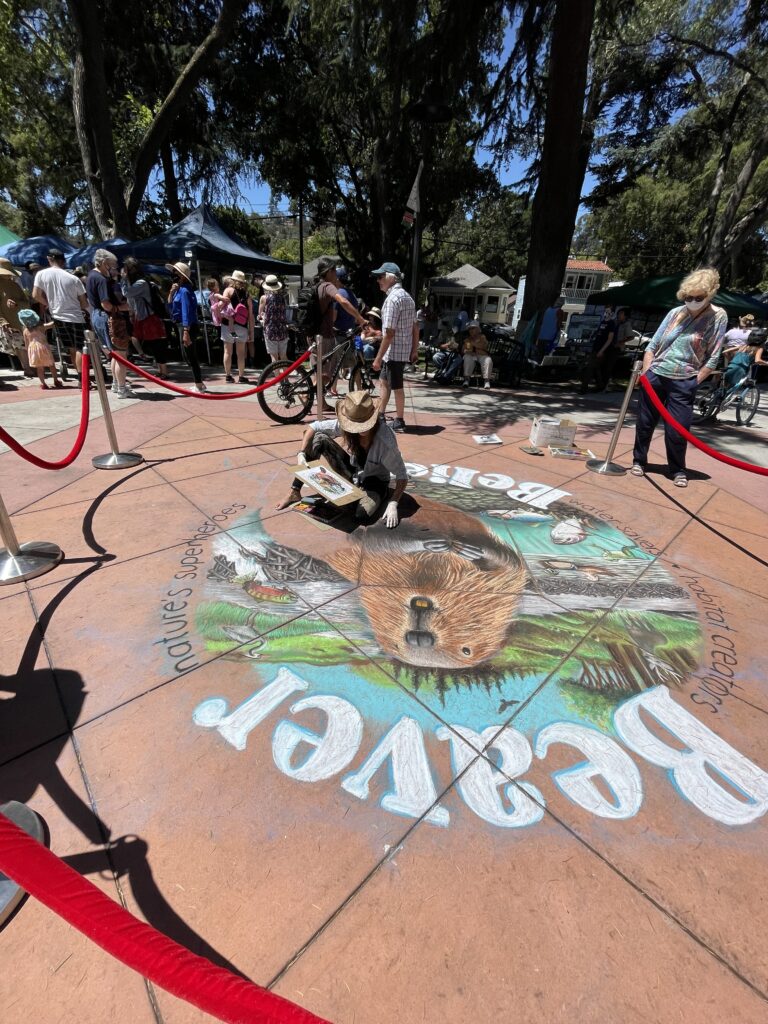
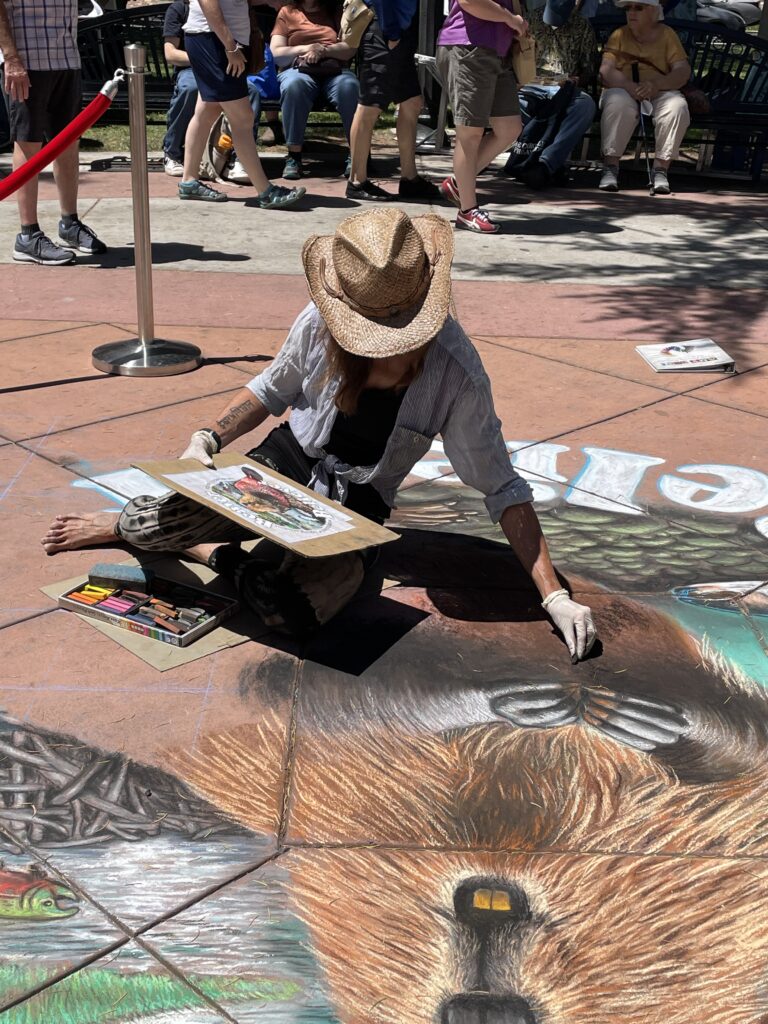
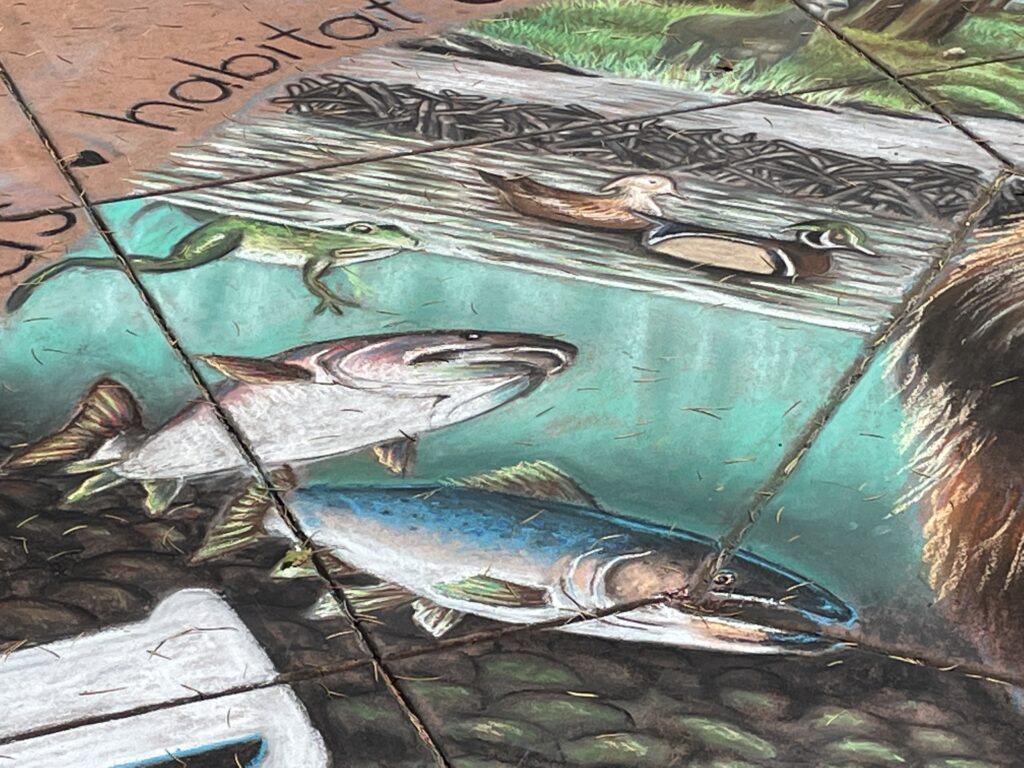
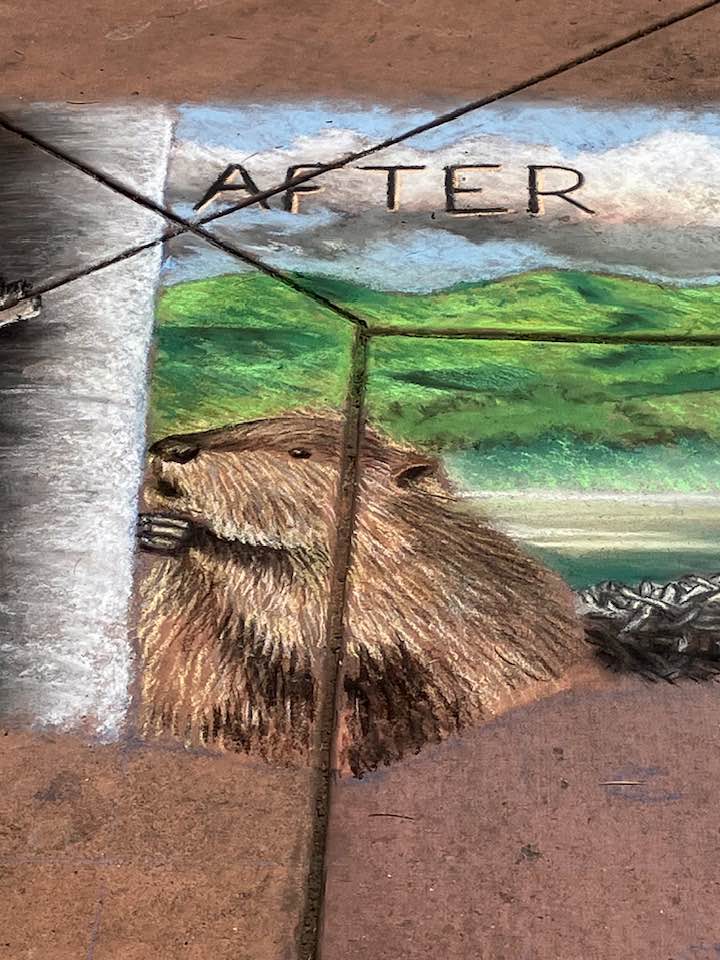
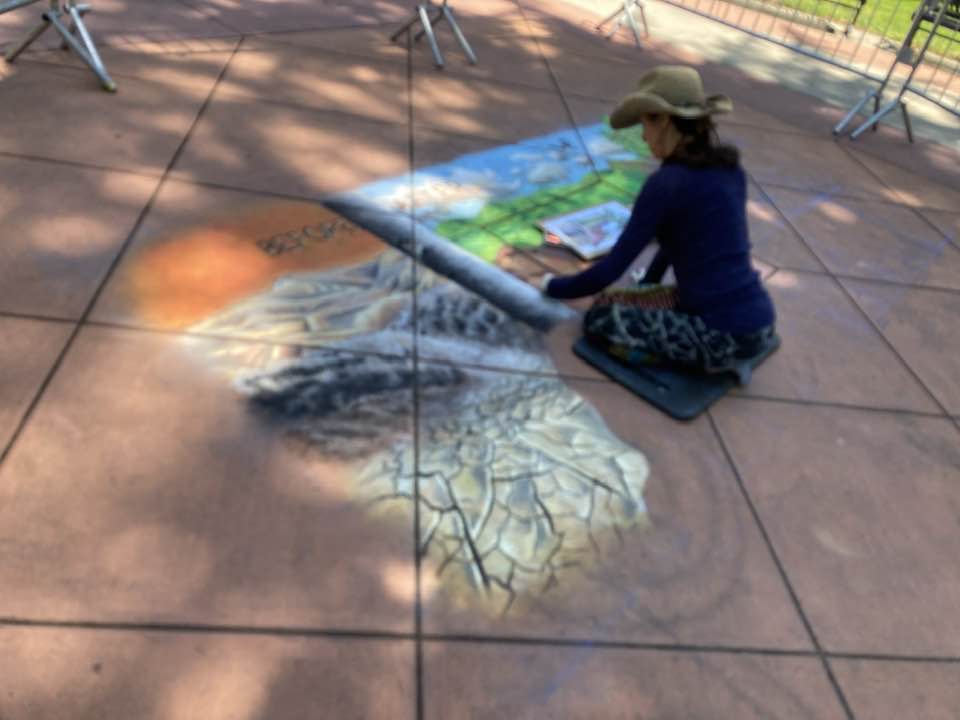
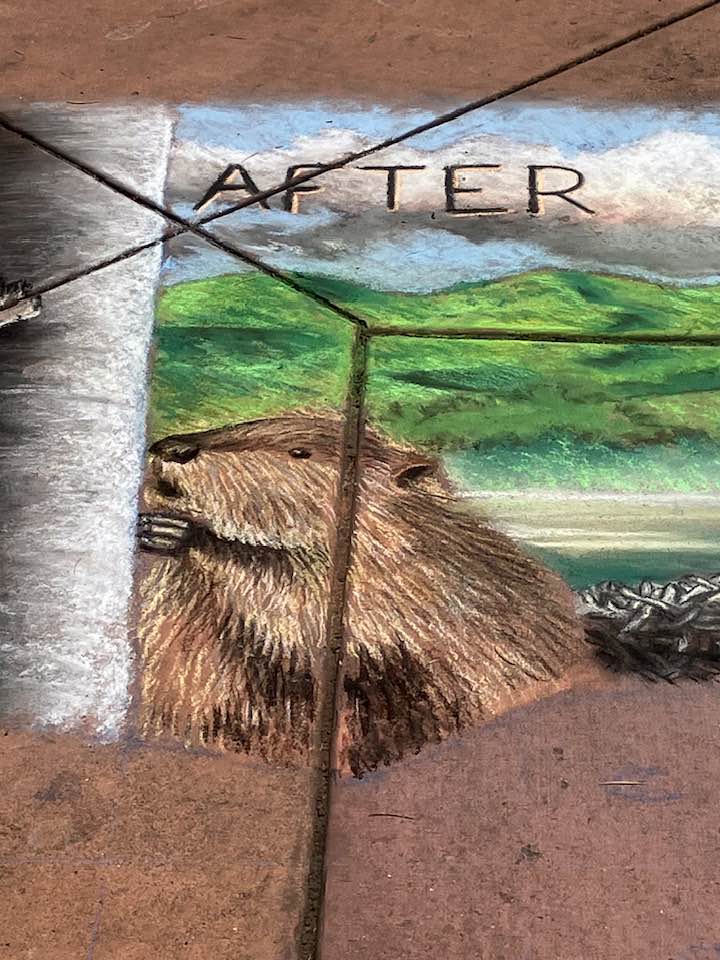
Well the SFEP started a creative artwork award this year to honor the creeks and raise awareness and I thought, HEY who on earth deserves an award more than the VERY HARDWORKING ARTIST Amy Hall who flies in for 24 hours ever year without pay and creates an unbelievable beaver mural in the middle of a crowded public event that washes away afterwards.
Creative Environmental Award
The Friends of the San Francisco Estuary announced a call for artists to submit work for the State of the San Francisco Estuary Conference, a local conference showcasing the science and need for action to protect the San Francisco Estuary.
So I nominated her.
And we were notified this week that she WON! 2nd prize with a cool 200 dollars and a mention at their big upcoming conference. Amy said she can’t make that date work but arranged for her very sweet father to come accept it in her honor. Amy is very pleased and even though 2nd prize kind of reminds me of this and she deserves WAY more its a nice symbol both of how hard she’s worked and how important beavers are to creeks.
accept it in her honor. Amy is very pleased and even though 2nd prize kind of reminds me of this and she deserves WAY more its a nice symbol both of how hard she’s worked and how important beavers are to creeks.
So HURRAY for Amy and HURRAY for the SFEP and thanks Rusty Cohn for noticing that her and her husband sometimes came to the Napa creek to see the beavers which gave me the nerve to ask her in the first place!
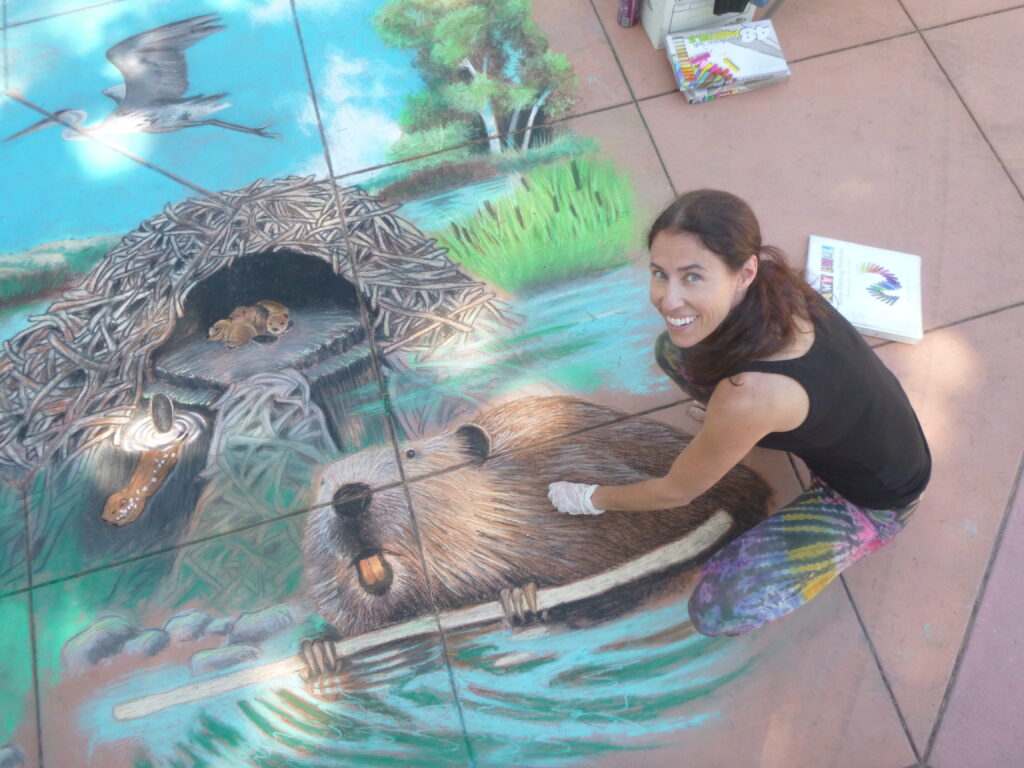
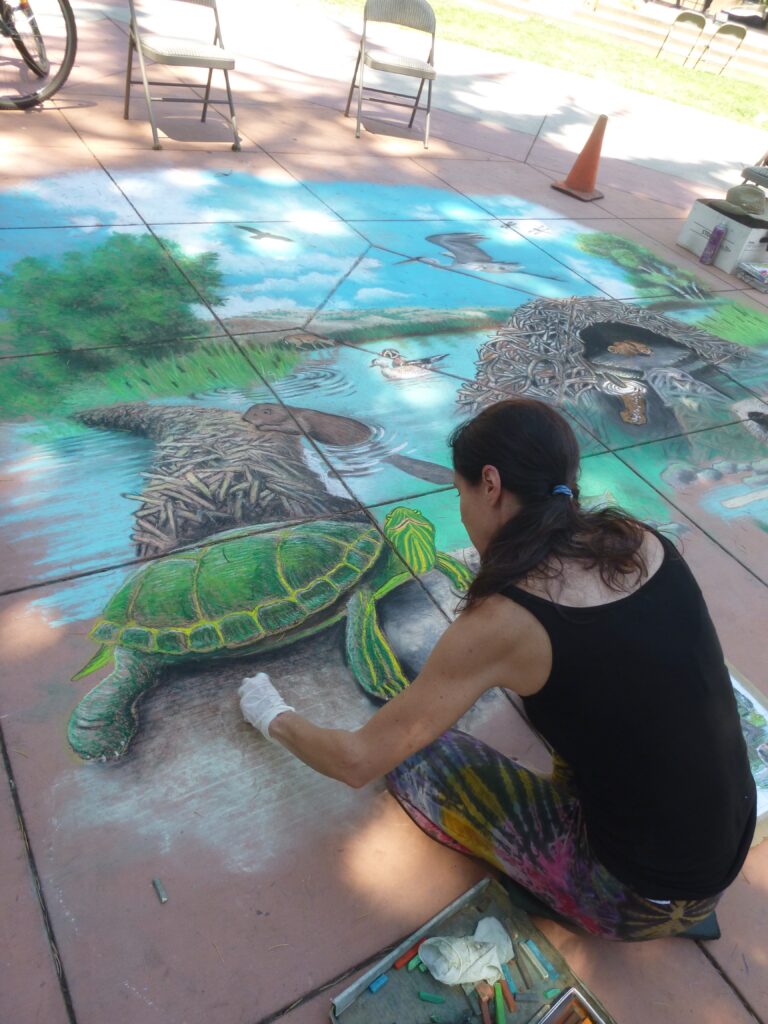
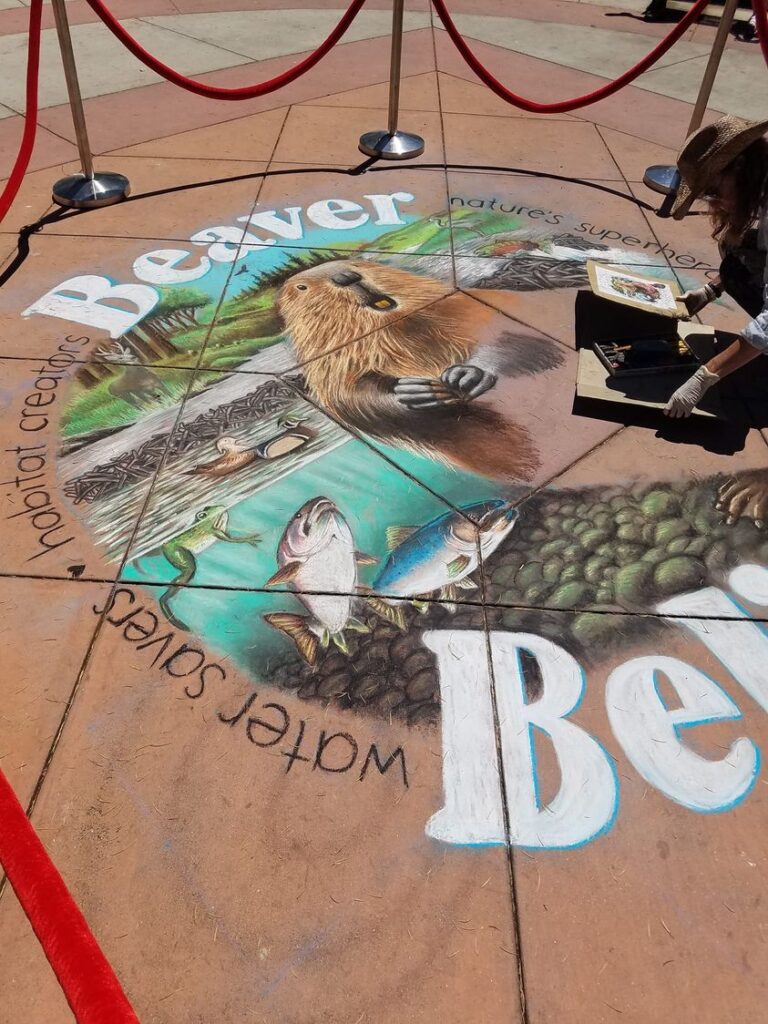
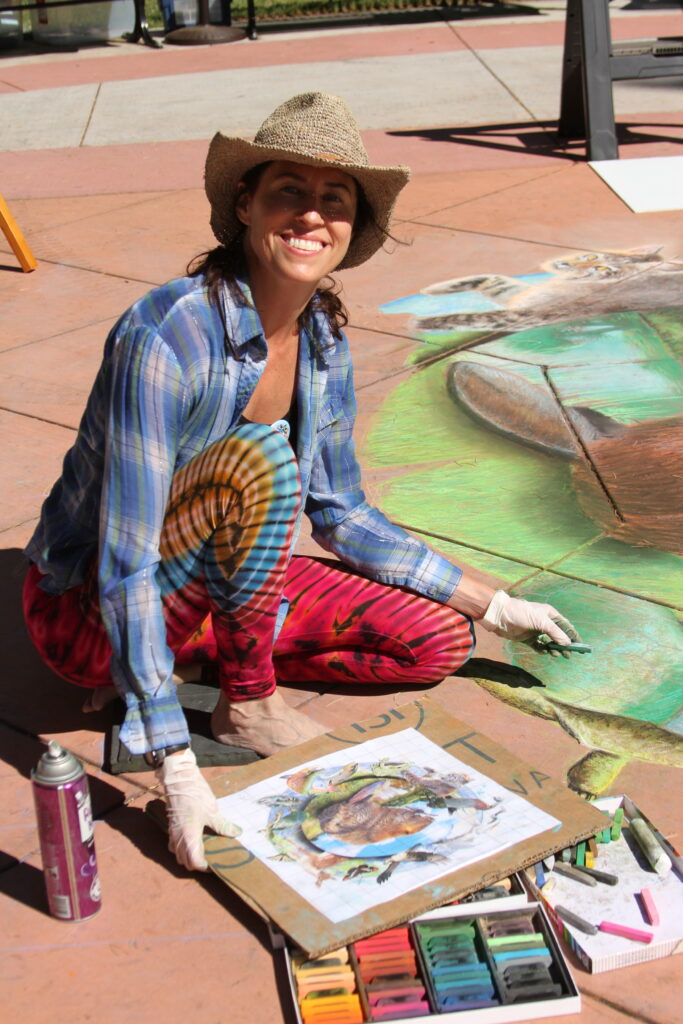
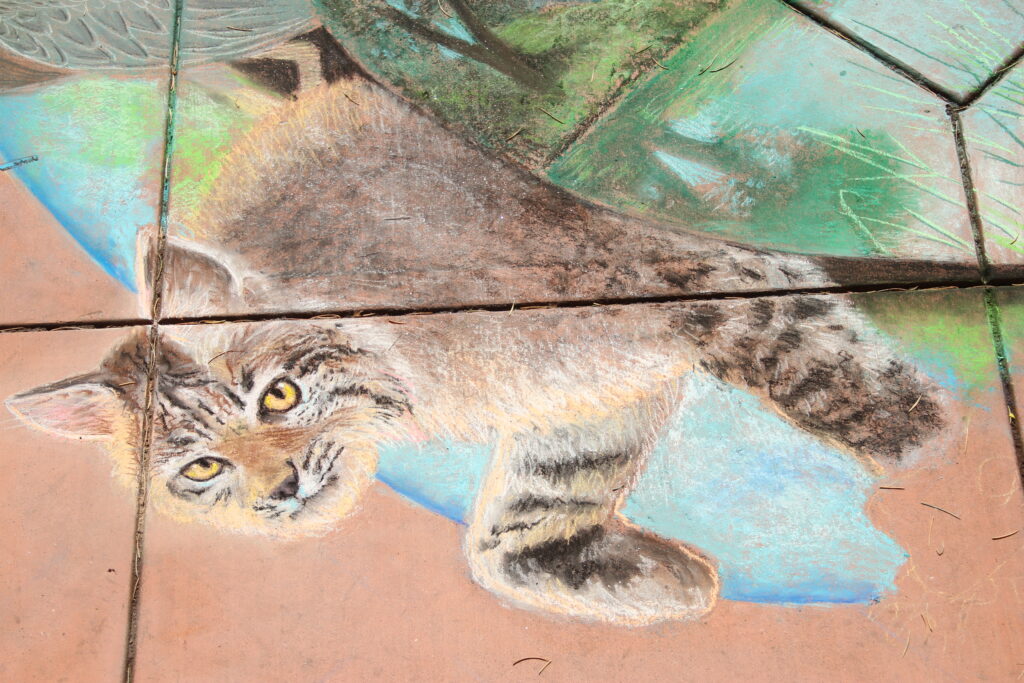
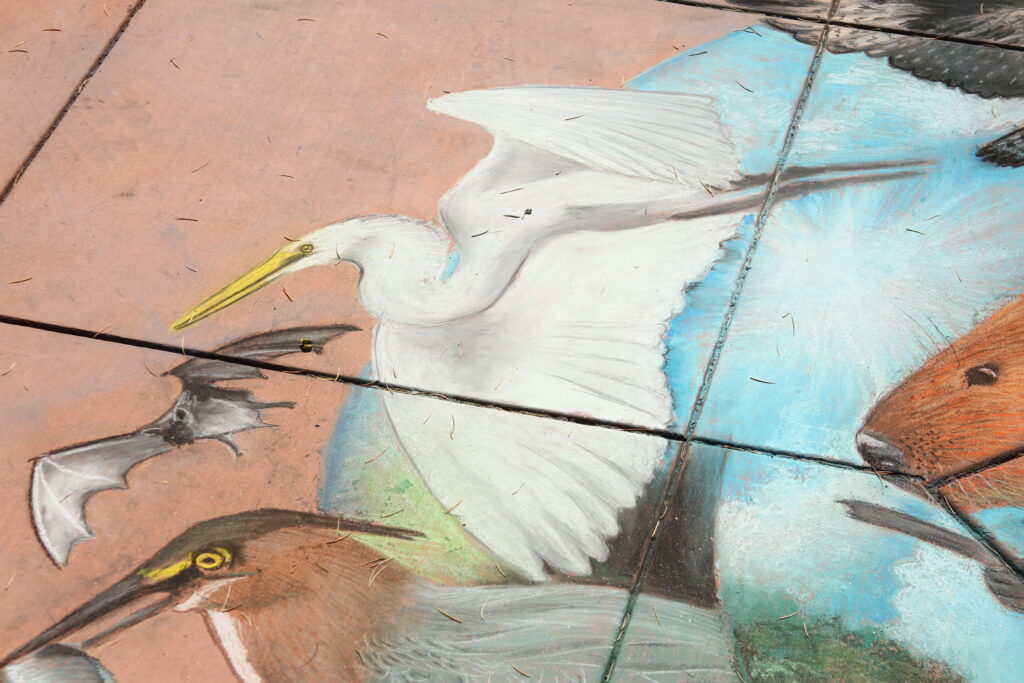
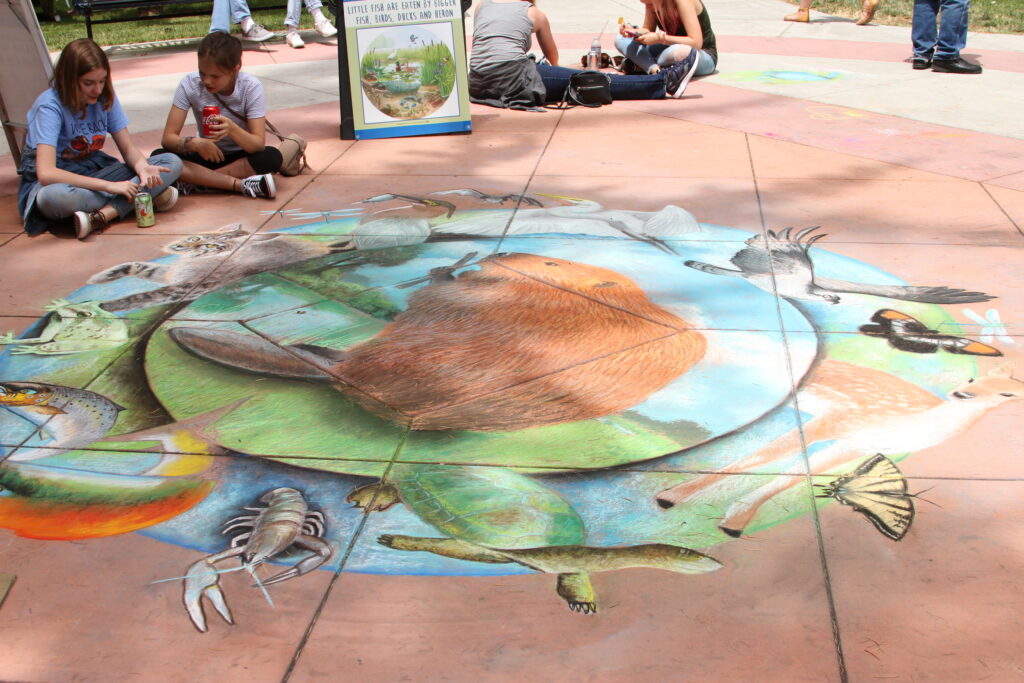
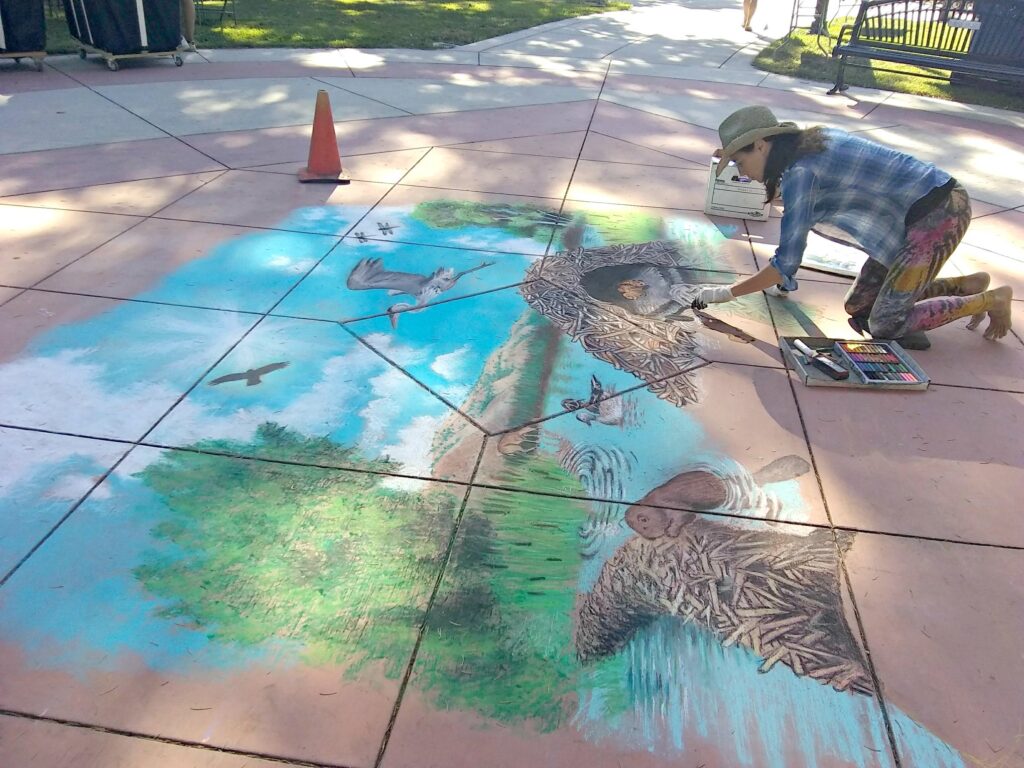























 Beaver lodges are built mainly for beavers and their families, but they often receive visits from other animals.Along streams, rivers, ponds, and lakes, beavers builds their lodges. They may look like a pile of twigs.
Beaver lodges are built mainly for beavers and their families, but they often receive visits from other animals.Along streams, rivers, ponds, and lakes, beavers builds their lodges. They may look like a pile of twigs.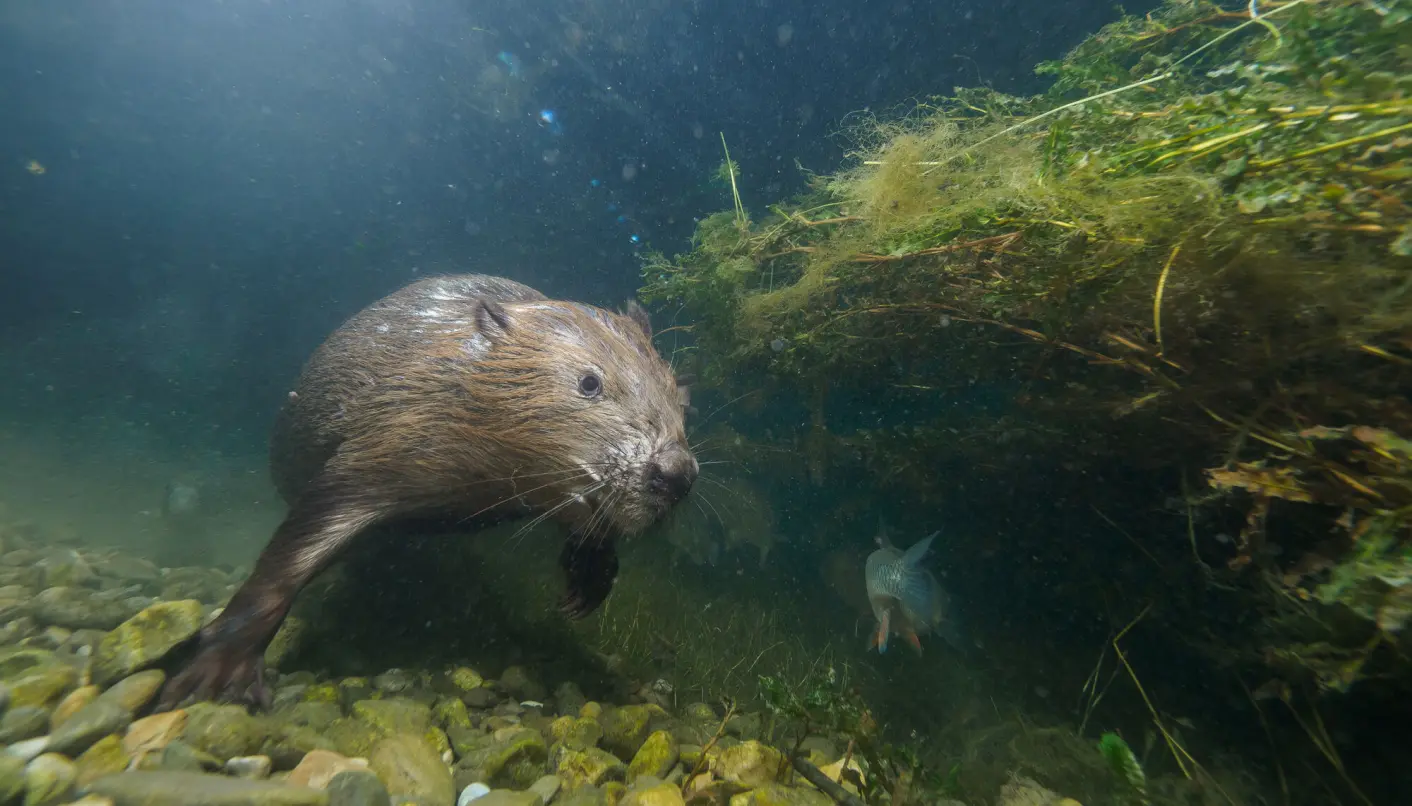

 A group of beavers searches for the cause of the death of the animal and plant species that inhabit the river where they live. The river is sick, but no one knows why. Moi, the little beaver, embarks on a dangerous journey upriver to find the source of the illness. Will he be able to bring his beloved river back to life? This endearing story denounces the threat and destruction suffered by nature due to the destructive power of man.
A group of beavers searches for the cause of the death of the animal and plant species that inhabit the river where they live. The river is sick, but no one knows why. Moi, the little beaver, embarks on a dangerous journey upriver to find the source of the illness. Will he be able to bring his beloved river back to life? This endearing story denounces the threat and destruction suffered by nature due to the destructive power of man. Habia una vez (Once upon a time) un largo rio de limpias y claras andando andando trasaba de parte de parte) there was a long, clear river, flowing from one side to the other) a un imenso bosque tan imenso de a ninguna de sus moradores en la habia en la corrido pensar que pudiese tener limites.(through an immense forest so vast that none of its inhabitants could have imagined it could have any limits).
Habia una vez (Once upon a time) un largo rio de limpias y claras andando andando trasaba de parte de parte) there was a long, clear river, flowing from one side to the other) a un imenso bosque tan imenso de a ninguna de sus moradores en la habia en la corrido pensar que pudiese tener limites.(through an immense forest so vast that none of its inhabitants could have imagined it could have any limits). A ranch owner thanked his neighbors for being wild animals — and that’s because the beavers have helped keep his plants under control.
A ranch owner thanked his neighbors for being wild animals — and that’s because the beavers have helped keep his plants under control.